- GST No. 24ABHPD0245L1ZZ
- Send SMS
- Send Email
| Business Type | Manufacturer, Exporter, Supplier, Retailer, Wholesaler |
| Brand Name | NoeDAF |
| Product Code | NeoDAF |
| Payment Terms | L/C, T/T |
Preferred Buyer From
| Location | Worldwide |
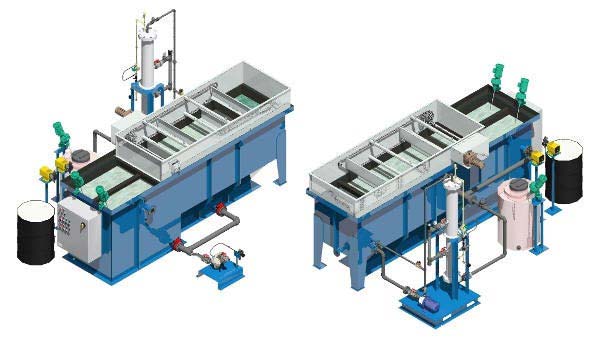
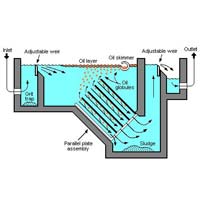
NeoTech DAF process consists of super saturation of discharge water from the effluent end of the system tank with air. The super saturated water stream is then mixed with the waste stream and pressurized in pressure tube. A sudden release of pressure from the saturated stream millions of microscopic bubbles form and attach themselves to the contaminants of oil and solids in the wastewater, thereby changing their buoyancy and floating them to the water surface where they can be skimmed and removed from the water. NeoTech also offer a combined chemical pretreatment to improve DAF solids removal efficiencies.
Features :
- The use of chemical flocculants with DAF is based on system efficiency, application contaminant characteristics and cost. Chemical pretreatment often improves DAF solids removal efficiencies. The use of chemical flocculants with DAF is based on system efficiency, application (use of DAF) contaminant characteristics and cost.
- Commonly used chemicals include trivalent metallic salts of iron, such as FeCI2 or FeSO4 or aluminum, such as AISO4. Organic and inorganic polymers (cationic or anionic) are often used to enhance the flotation process. The most commonly used inorganic polymers are the polyacrylamides.
- Attachment of most of the bubbles to solid particles can be effected through surface energies while others are trapped by the solids or by hydrous oxide flocs as the floc spreads out in the water column. Colloidal solids are normally too small to allow formation of sufficient air-particle bonding.
- They must first be coagulated by a chemical such as the aluminum or iron compounds mentioned above and then absorbed by the hydrous metal oxide floc generated by these compounds. Frequently the coagulant is required in combination with the flocculant.
Optional Facility :
- 304/316 Stainless Construction
- Emulsion Breaking System
- Chemical Pretreatment
- Sludge Pump out
- Float Pump out
- Effluent Pump out
- Influent Feed
- pH Adjustment System
Looking for "Dissolved Air Flotation System" ?
Set(s)